How to Design a High-Performance LAN, WAN, and Wi-Fi Network for Your Business
Why Network Performance Matters
In today’s digital-first world, network performance is the backbone of every business operation. From day-to-day communications to cloud applications and remote collaboration, a slow or unreliable network can cost companies productivity, customer satisfaction, and even revenue.
A high-performance network ensures:
- Seamless connectivity for all users, regardless of location
- Minimal downtime, avoiding costly disruptions
- Optimized application performance for cloud, VoIP, and collaboration tools
- Strong security to protect sensitive data and business operations
For businesses with multiple locations, remote employees, or bandwidth-intensive applications, the difference between a well-designed network and a poorly planned one can be substantial. That’s why careful LAN, WAN, and Wi-Fi network design is essential.
Key Considerations for LAN, WAN, and Wi-Fi Design
Designing a high-performance network starts with understanding your business needs, existing infrastructure, and growth plans. Here’s a breakdown of critical components:
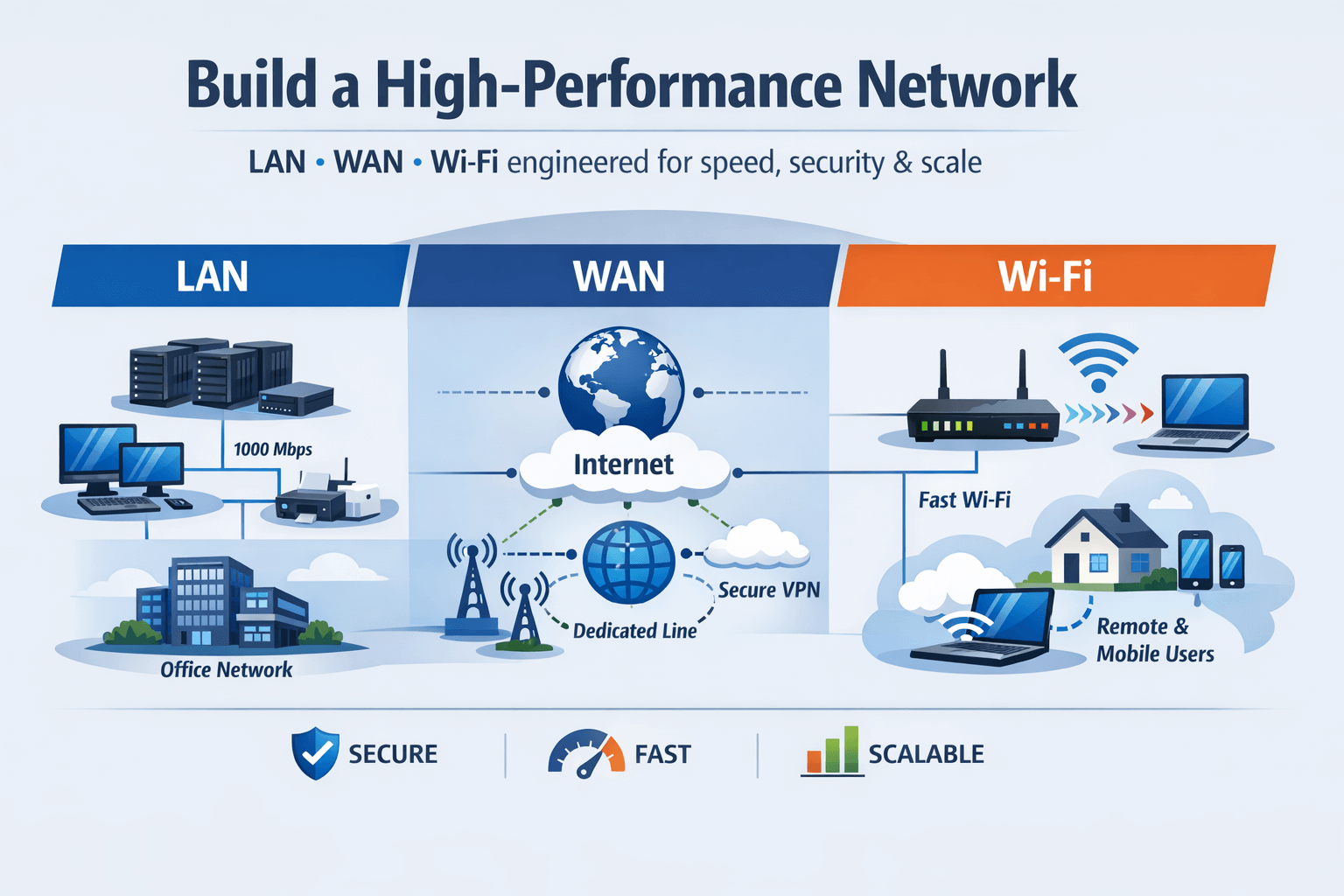
LAN (Local Area Network)
The LAN connects devices within your office or campus. Consider:
- Topology selection: Star, mesh, or hybrid, depending on office layout and scalability. For example, a mesh network may be ideal for offices with multiple floors or departments requiring high redundancy.
- Bandwidth planning: Ensure sufficient capacity to handle peak usage, video conferencing, and cloud applications. A simple office may need 1–10 Gbps, whereas larger setups may require 10–40 Gbps or more.
- Redundancy: Include backup switches, dual network paths, and failover configurations to minimize downtime during hardware failures.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN connects multiple offices, remote sites, or cloud services. Key considerations include:
- Reliable connectivity: Evaluate SD-WAN, MPLS, or dedicated leased lines to provide consistent performance across sites.
- Optimized routing: Use intelligent routing to reduce latency for cloud-based apps and VoIP communications.
- Security: Encrypt traffic and deploy firewalls at each site to protect data across the network.
Example: A company with three regional offices might use SD-WAN for cost-effective routing while maintaining high uptime and consistent performance for video calls and ERP systems.
Wi-Fi Network
Wi-Fi is no longer just a convenience—it’s a critical business tool. Proper design ensures coverage, speed, and reliability:
- Coverage planning: Map office spaces to avoid dead zones using Wi-Fi heatmaps.
- Access point placement: Ensure signal strength while avoiding interference from walls, furniture, or other electronics.
- Performance monitoring: Use Wi-Fi controllers and analytics tools to continuously track usage, detect interference, and adjust settings.
Tip: Separate guest Wi-Fi from corporate Wi-Fi to protect sensitive systems while offering visitors seamless connectivity.
Tools and Technologies for Network Optimization
Maintaining high network performance requires ongoing monitoring and optimization. Recommended tools include:
- Network monitoring software: Tools like PRTG, SolarWinds, or Nagios help detect bottlenecks, monitor traffic, and generate alerts in real-time.
- Performance testing tools: Regular speed tests and latency checks ensure that network changes or expansions don’t negatively impact performance.
- Load balancing solutions: Distribute traffic efficiently across servers and connections to prevent single points of failure.
- Network security devices: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs help protect sensitive data while maintaining performance.
Best Practices for High-Performance Networks
To ensure your network remains fast, reliable, and secure:
- Plan for the future: Account for anticipated growth in users, devices, and applications.
- Segment networks: Use VLANs or subnets to reduce congestion and improve security.
- Implement Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritize critical traffic like VoIP or cloud applications.
- Regular audits and updates: Periodically review hardware, firmware, and configurations to prevent performance degradation.
- Train staff: Educate employees on network best practices, including proper Wi-Fi usage and avoiding bandwidth-heavy activities during peak hours.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-designed networks can fail if certain pitfalls are overlooked:
- Overcomplicating the network with unnecessary hardware or complex configurations
- Neglecting network security, leaving sensitive data exposed
- Failing to plan for future growth, causing congestion as the business scales
- Ignoring monitoring and maintenance, leading to undetected issues
Real-World Example
Consider a mid-sized business with 150 employees across three floors. Initially, the network experienced frequent Wi-Fi dropouts and slow access to cloud services. After redesigning their LAN/WAN architecture, optimizing access point placement, and implementing SD-WAN with QoS rules:
- Video conferencing became smooth and reliable
- Cloud applications ran without delays
- Downtime dropped by 70%
This demonstrates how strategic network design improves productivity, security, and overall business performance.
Conclusion
Designing a high-performance LAN, WAN, and Wi-Fi network is more than just connecting devices—it’s about building a reliable, secure, and scalable foundation for your business. With careful planning, monitoring, and optimization, your network can support current operations and future growth.
Ready to build a network that keeps your business running at peak performance?
👉 Contact us today to discuss your network infrastructure needs and let our experts design a solution tailored to your business.

